


West Francia Kingdom – Frankish Empire – 21st Century – Kingdom of the Franks – Imperium Francorum The West Francia Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the West Franks or the West Frankish Kingdom, was a medieval European kingdom that played a crucial role in the history of the early Middle Ages. It emerged as a distinct political entity in the 9th century and represented the western part of the Carolingian Empire after the division of Charlemagne's vast realm. The history of the West Francia Kingdom is marked by political turmoil, Viking invasions, and the gradual development of the medieval feudal system. The Kingdom of the Franks (Latin: Regnum Francorum), also known as the Frankish Kingdom, the Frankish Empire (Latin: Imperium Francorum) or Francia, was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties during the Early Middle Ages. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era.
The West Francia Kingdom came into existence in the aftermath of the Treaty of Verdun in 843. The Treaty of Verdun divided the Carolingian Empire, established by Charlemagne, into three parts, with West Francia corresponding to the western territories. Lothair I, the eldest son of Charlemagne, received the central portion of the empire, while Louis the German was granted the eastern part. Charles the Bald, the youngest son, became the ruler of West Francia. At the time of its establishment, West Francia faced numerous challenges. The kingdom's borders were constantly under threat from Viking raids, which had become a frequent occurrence during the 9th and 10th centuries. The Vikings' incursions disrupted trade and agriculture, leading to widespread insecurity and economic decline. The West Francia Kingdom struggled to defend its territory and maintain stability against these external threats One of the notable rulers of West Francia was Charles the Simple, who reigned from 898 to 922. His reign marked a particularly turbulent period in the kingdom's history. Charles faced internal strife, as powerful nobles vied for control over various regions. In 911, Charles made the fateful decision to grant the Viking chieftain Rollo a territory in Normandy, known as the Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte. This agreement led to the establishment of the Duchy of Normandy and the beginnings of the Norman presence in France. Throughout the 10th century, the West Francia Kingdom continued to weaken, as the power of the central monarchy eroded. Local nobles gained increasing autonomy and control over their territories, and the king's authority diminished. This process of decentralization laid the groundwork for the development of the feudal system, characterized by a hierarchy of lords who swore loyalty to more powerful overlords. By the early 11th century, the West Francia Kingdom had become fragmented into numerous smaller feudal domains, each ruled by a local lord. The monarchy's power was largely symbolic, and the kings were often weak figures who lacked the means to exert their authority. This period also saw the emergence of the Capetian Dynasty, with Hugh Capet being crowned King of the Franks in 987. The Capetian kings gradually consolidated their control over the region, laying the foundation for the future Kingdom of France. The Demise of Nobility in France The demise of nobility in France is a significant historical phenomenon that unfolded over centuries, ultimately leading to the transformation of the French social and political landscape. This transformation was characterized by a decline in the privileges, power, and influence of the traditional aristocracy, which had long held a prominent role in French society. The demise of nobility in France can be attributed to a complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors that evolved over time. One of the key factors contributing to the decline of nobility in France was economic change. The traditional privileges of the nobility, including tax exemptions and land ownership, were increasingly seen as burdensome by the growing middle class and commoners. The nobility enjoyed significant tax exemptions, which shifted the tax burden onto the lower classes, leading to social discontent. Moreover, the French economy began to undergo significant changes during the late Middle Ages and early modern period, transitioning from a primarily agrarian society to one marked by the growth of trade and industry. This shift diminished the economic importance of land ownership, which had been a cornerstone of noble wealth and influence. The political landscape of France also played a crucial role in the demise of nobility. The monarchy, under strong monarchs like Louis XIV, sought to centralize power and weaken the influence of regional nobles. The monarchy imposed greater control over the nobility through measures such as the system of intendants, who were royal officials appointed to oversee and regulate the provinces. Additionally, Louis XIV's construction of the Palace of Versailles served as a symbol of royal power and a means of keeping the nobility under close watch, as they were often required to reside at the court. The emergence of modern warfare also contributed to the decline of the nobility in France. The advent of professional armies and the centralization of military power in the hands of the state diminished the importance of feudal knights and their private armies. The concept of a citizen army, where commoners were conscripted to serve in the military, further undermined the traditional military role of the nobility. The Enlightenment and the spread of new ideas also played a significant role in challenging the legitimacy of the nobility. Philosophers and thinkers of the Enlightenment promoted notions of equality, individual rights, and meritocracy, which directly contradicted the entrenched privileges of the nobility. Enlightenment ideas influenced public opinion and contributed to the sentiment that the nobility's privileges were unjust and outdated. One of the most pivotal events in the demise of nobility in France was the French Revolution of 1789 . The revolution was driven by widespread social and economic inequality, and it aimed to abolish the privileges of the nobility. The Revolution led to the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which proclaimed equality and liberty for all citizens, regardless of social class. The nobility faced severe consequences during the Reign of Terror, with many nobles losing their lives or fleeing the country. Following the French Revolution, the Napoleonic era further accelerated the decline of the nobility. Napoleon Bonaparte promoted a meritocratic system, where individuals were promoted based on their abilities and achievements rather than their social status. He dismantled feudal privileges and established a more centralized administrative system. The demise of nobility in France was a protracted process that spanned several centuries, culminating in the radical changes brought about by the French Revolution and the Napoleonic era. While the traditional aristocracy lost much of its power and privilege, it did not completely disappear. Instead, it transformed into a different social class, adapting to the changing political and social landscape of France. Today, the French nobility remains a part of the country's historical legacy, with its influence significantly diminished but not entirely eradicated. rance no longer officially recognizes hereditary noble titles or grants new ones. The French Revolution, which began in 1789, marked the end of the feudal system and the privileges associated with nobility in France. During the revolution, many nobles lost their titles, properties, and even their lives. The abolition of hereditary noble titles was a fundamental aspect of the revolutionary ideals of equality and the rejection of the old feudal system. The revolutionaries aimed to create a society where individuals were equal under the law, regardless of their birth or social status. As a result, hereditary nobility and aristocratic titles were abolished, and the concept of nobility was disestablished in France. In the aftermath of the French Revolution and the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, the Napoleonic Code (Code Napoléon) was implemented, which further solidified the legal framework that did not recognize noble titles. The Napoleonic Code laid the foundation for modern French civil law and emphasized legal equality among citizens. While hereditary noble titles are no longer officially recognized in France, some individuals may still use their historical titles informally or as a matter of personal identity or tradition. These titles, however, have no legal standing or privileges attached to them in contemporary French law. France is now a republic with a strong emphasis on egalitarian principles, and noble titles hold no legal or official significance within the country's legal and political framework. The tiny Frankish nation in the Pyrenees mountains is Andorra. Andorra is a landlocked microstate located in southwestern Europe, nestled in the eastern Pyrenees between France and Spain. It is one of the smallest countries in the world by land area and population. Andorra is known for its beautiful mountainous landscapes, skiing resorts, and a unique co-principality system of governance where it is jointly ruled by two co-princes: the President of France and the Bishop of Urgell in Spain. Despite its small size, Andorra has a thriving tourism industry and a unique cultural blend influenced by both French and Catalan-Spanish traditions. The President of France's role as co-prince of Andorra is largely ceremonial, and it does not grant them any authority or power within Andorra's domestic affairs. The Bishop of Urgell also holds a similar symbolic position. The actual governance of Andorra is carried out by its own government and institutions. Declaration of Independence and the Establishment of the Channel Island Micronation of Blondeleburg or West Francia We, the proud inhabitants of the Channel Island Fief of Blondel, West Francia, in the 21st century, in the spirit of self-determination, freedom, and the preservation of our unique cultural heritage, hereby declare our independence and the establishment of the Channel Island Micronation if it be so deemed legal herein with international law as per the sovereigny of a Crown Holding if it be so deemed legal under international laws. This historic declaration signifies our emergence as a sovereign entity, with our own West Francia royal monarchy, and carries with it the inheritance of the Kingdom of West Francia, a legacy that has lain dormant for centuries. Preamble For centuries, the Fiefs of the Channel Islands have stood as bastions of autonomy and resilience, with a storied history that traces its roots back to the Duchy of Normandy. The islands' distinctive character, culture, and traditions have been nurtured and preserved throughout the ages. Today, as we take this momentous step, we invoke the enduring spirit of our forebears who cherished our islands' unique identity. The Inheritance of West Francia In this declaration, we assert our legitimate claim to the legacy of the Kingdom of West Francia. The Kingdom of West Francia, a realm of rich history and culture, found its demise with the rise of revolutionary ideals in continental France, leading to the banishment of the nobility during the tumultuous period of the French Revolution. As the inheritors of this once-great kingdom, we carry forward its legacy as custodians of its history, traditions, and values. Presently, the BBC and other news is unclear if the State or Crown maintains any rights to foreshore or waters in Guernsey. Guernsey investigates taking seabed ownership from Queen - BBC News The Establishment of the Channel Island Micronation With this declaration, we establish the Channel Island Micronation as a sovereign entity, standing proudly among the family of nations. Our micronation shall be characterized by principles of democracy, individual rights, and a deep respect for the rule of law. We, the people of the Channel Island Micronation, solemnly commit to upholding these ideals as the foundation of our governance. The West Francia Royal Monarchy We proudly announce the revival of the West Francia royal monarchy, which shall reign as the cornerstone of our cultural heritage and symbol of our historical ties to the Kingdom of West Francia. The West Francia royal monarchy shall serve as a unifying force, reflecting our commitment to tradition, continuity, and the preservation of our unique identity. Recognition of Autonomy While acknowledging our historical relationship with the British Crown, we declare our autonomy and self-governing status as the Channel Island Micronation. We shall continue to maintain our close ties with the British Crown while also pursuing diplomatic relations with other nations to foster mutual understanding, cooperation, and collaboration. Conclusion In bearing witness to this declaration, we, the people of the Channel Island Micronation, reaffirm our commitment to our cherished values, traditions, and the enduring legacy of the Kingdom of West Francia. We stand united in our pursuit of a prosperous and harmonious future, where our cultural heritage and autonomy shall be preserved for generations to come. May this declaration serve as an enduring testament to our determination, resilience, and the indomitable spirit of the Channel Islands. Signed on this day, the Jan 1st 2019 George Mentz, Esq. - Seigneur of Fief Blondel of the Channel Island Micronation of Blondelenburg www.WestFrancia.com Rulers of West Francia 1. Charles the Bald (843-877): Charles was the first ruler of West Francia after the Treaty of Verdun in 843, which divided the Carolingian Empire. He became the King of the West Franks. 2. Louis the Stammerer (877-879): Louis II succeeded his father, Charles the Bald, as King of West Francia. 3. Louis III (879-882): Louis III, also known as Louis the Younger, followed his brother Louis the Stammerer as King of West Francia. 4. Carloman II (879-884): Carloman II ruled alongside his brother Louis III but died prematurely. 5. Charles the Fat (884-888): Charles the Fat, another son of Louis the Stammerer, reunited West Francia with the other Carolingian realms. 6. Odo of France (888-898): Odo, also known as Eudes, became King of West Francia after the Carolingian dynasty faced internal conflicts. 7. Charles the Simple (898-922): Charles the Simple succeeded Odo and ruled during a turbulent period marked by Viking invasions. 8. Robert I (922-923): Robert I, known as Robert of France, briefly took the throne after Charles the Simple. 9. Rudolph of France (923-936): Rudolph became King of West Francia after Robert I. 10. Louis IV (936-954): Louis IV, often referred to as Louis from Overseas, assumed the throne. 11. Lothair (954-986): Lothair ruled for an extended period, consolidating power and facing various challenges during his reign. 12. Louis V (986-987): Louis V succeeded his father, Lothair, as King of West Francia but died prematurely. 13. Hugh Capet (987-996): Hugh Capet, founder of the Capetian dynasty, became King of the Franks and established the House of Capet. 14. Richard II, Duke of Normandy (996-1026): Richard II succeeded his father, Richard I, as Duke of Normandy during Hugh Capet's reign. 15. Robert I, Duke of Normandy (1027-1035): Robert I, also known as Robert the Magnificent, was the son of Richard II and ruled Normandy during this period. 16. William I, Duke of Normandy (1035-1087): William, famously known as William the Conqueror, became Duke of Normandy in 1035. In 1066, he successfully invaded England, becoming William I of England while retaining his position as Duke of Normandy. 17. William II, Duke of Normandy (1087-1106): William II, also called William Rufus, succeeded his father William I in both the English and Norman thrones. 18. Henry I, Duke of Normandy (1106-1135): Henry I, William the Conqueror's youngest son, ruled both England and Normandy. His reign marked the beginning of strained relations between the English and Norman branches of the royal family. 19. Stephen of Blois (1135-1144): Stephen of Blois, a grandson of William the Conqueror, briefly ruled Normandy but faced conflict in both England and Normandy during his reign. 20. Henry II, Duke of Normandy (1150-1189): Henry II, the first Plantagenet king, inherited the English throne and regained control of Normandy, effectively unifying the two territories under one ruler. 21. Richard I, Duke of Normandy (1189-1199): Richard the Lionheart, the son of Henry II, ruled both England and Normandy but spent much of his reign abroad, including during the Third Crusade. 22. John, Duke of Normandy (1199-1204): John, also known as John Lackland, succeeded his brother Richard I as Duke of Normandy but faced significant challenges, eventually losing Normandy to the King of France. 23. Philip II of France (1204-1223): Philip II, known as Philip Augustus, took control of Normandy from John Lackland in 1204. This marked the end of Norman rule in the region.. 24. Philip II of France (1180-1223): Philip II, also known as Philip Augustus, integrated Normandy into the Kingdom of France in 1204. 25. Louis VIII of France (1223-1226): Louis VIII succeeded his father, Philip II, as King of France and continued to rule over the integrated Normandy. 26. Louis IX of France (1226-1270): Louis IX, commonly known as Saint Louis, maintained the administration of Normandy as part of the French kingdom during his reign. 27. Philip III of France (1270-1285): Philip III continued to govern French Normandy as part of his broader reign over France. 28. Philip IV of France (1285-1314): Philip IV, also known as Philip the Fair, ruled over French Normandy as part of his efforts to centralize royal authority. 29. Louis X of France (1314-1316): Louis X briefly succeeded his father, Philip IV, but his reign was short-lived. 30. Philip V of France (1316-1322): Philip V followed his brother, Louis X, and continued to rule over integrated Normandy. 31. Charles IV of France (1322-1328): Charles IV, the last of the Capetian dynasty, also ruled Normandy during his short reign. 32. Philip VI of France (1328-1350): Philip VI, the first Valois king, assumed control over French Normandy. 33. John II of France (1350-1364): John II succeeded Philip VI and continued to govern the integrated Normandy. 34. Charles V of France (1364-1380): Charles V, known as Charles the Wise, ruled over French Normandy and focused on restoring the monarchy's strength. 35. Charles VI of France (1380-1422): Charles VI faced significant challenges during his reign, including the Hundred Years' War, which also affected Normandy. 36. Charles VII of France (1422-1461): Charles VII's reign saw the gradual recovery of French territories, including Normandy, from English control during the Hundred Years' War. 37. Louis XI of France (1461-1483): Louis XI continued the process of consolidating royal authority in French Normandy. 38. Charles VIII of France (1483-1498): Charles VIII's reign saw the return of Normandy to the French crown, as it was under Burgundian control for a time. 39. Louis XII of France (1498-1515): Louis XII ruled over Normandy and initiated reforms during his reign. 40. Francis I of France (1515-1547): Francis I's reign saw further centralization of power and governance of French Normandy. 41. Henry II of France (1547-1559): Henry II ruled during a period of religious conflict in France, but Normandy remained integrated into the kingdom. 42. Francis II of France (1559-1560): Francis II's reign was brief and marked by religious strife, but Normandy remained part of the French kingdom. 43. Charles IX of France (1560-1574): Charles IX faced the French Wars of Religion during his reign but ruled over integrated Normandy. 44. Henry III of France (1574-1589): Henry III also ruled during the French Wars of Religion and continued to govern Normandy as part of France. 45. Henry IV of France (1589-1610): Henry IV, the first monarch of the Bourbon dynasty, consolidated royal power and administered Normandy as part of the French realm. 46. Louis XIII of France (1610-1643): Louis XIII's reign saw the continuation of centralized rule over Normandy. 47. Louis XIV of France (1643-1715): Louis XIV, the Sun King, further centralized governance in France, including Normandy. 48. Louis XV of France (1715-1774): Louis XV ruled over integrated Normandy during the 18th century. 49. Louis XVI of France (1774-1792): Louis XVI was the last Bourbon king of France before the French Revolution. 50. French First Republic (1792-1804): After the French Revolution, France became a republic, and Normandy was administratively reorganized. 51. Napoleon Bonaparte (1804-1814/1815): Napoleon Bonaparte became Emperor of the French, and Normandy was integrated into the French Empire. 52. Restoration of the Bourbon Monarchy (1814-1830): After the fall of Napoleon, the Bourbon monarchy was briefly restored in France, and Normandy remained part of the kingdom. 53. July Monarchy (1830-1848): The July Monarchy continued to govern Normandy until the 1848 revolution. 54. French Second Republic (1848-1852): The French Second Republic led to the establishment of a republic, with Normandy as part of its territory. 55. Second French Empire (1852-1870): Under Napoleon III, the Second French Empire included Normandy. 56. French Third Republic (1870-1940): French Normandy was part of the Third Republic until the outbreak of World War II. 57. Vichy France (1940-1944): During World War II, Vichy France controlled Normandy for a period. 58. 1945 - Liberation of Channel Islands and Normandy by American Forces including Sgt. Judge Henry A Mentz Jr with Patton's Army. 59. Present Day West Francia - Comm'r George Mentz who is the Noble Seigneur of The Fief de Blondel or Blondelenburg which owns land and foreshore and seastead and territorial waters in Ancient Normandy West Francia - 2018 www.WestFrancia.com - As nobility abolished in France and Gaul except for in the Channel Islands, The Fief Blondel, which is in a "Non-EU" and "Non-UK jurisdiction", has made claim as the hereditary nation and Kingdom of West Francia. To this date, The island of Guernsey is among the last remnants of the historical territories associated with the Duchy of Normandy that still maintain the practice of granting noble titles. These islands have a unique historical and legal status, which allows them a degree of autonomy and self-governance. This autonomy has enabled them to retain certain historical customs and practices, including the recognition of noble titles. The Channel Islands, including Guernsey, were historically part of the Duchy of Normandy, which was a medieval duchy in northern France. When William the Conqueror, Duke of Normandy, became William the Conqueror, King of England, in 1066, the Channel Islands remained possessions of the English Crown. The Titular and Hereditary Seigneur of West Francia is George Mentz - Mentz is a blood descendant of the following Kings of Normandy, France, and England . Henry KING OF ENGLAND, DUKE OF NORMANDY I 29th mggf, 1070 - 1135AD, Philip IV "The Fair" King of France 1268 - 1314AD, William the Conqueror, Robert II ("The Pious" King of France) Capet 0972 - 1031, King Robert I Capet the strong Count of Paris and Poitiers of France de Marvals 866 - 931, Hugh Capet King of France 0915 - 1031AD, Robert I 'The Magnificent' 'The Devil' KING OF NORMANDY,DUKE I 17th ggf 999 - 1035AD, Henry KING OF ENGLAND, DUKE OF NORMANDY I 29th mggf 1070 - 1135AD, Phillippe III le Hardi "The Bold" King of France Capet Capet 1245 - 1285AD, Louis IX Capet de Bourbon, King of France 1465 - 1500AD, Louis VIII King of France 1187 - 1226, Philip II of France King of France 1165 - 1223AD, Henry I of France - King of Franks 1008 - 1060AD, Louis VIII King of France 1120 - 1180AD, King Louis VI King of France 1081 - 1137AD, Philip I of France King of Franks 1052 - 1108, Louis VIII King of France 1187 - 1226AD, Louis IX of France King of France 1214 - 1270, Henry II of France 1519 - 1559, Rollo The Viking Chief Duke of Normandy 870–932 BIRTH 870 DEATH 932 30th great-grandfather, Nicola Orsini Orsini ( 3rd Count of Nola, grand Justiciar and also Grand Chancellor of the Kingdom of Naples descendants of first 5 Roman emperors who controlled West Francia and Gaul. Kingdom of Franks - History In history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: Francia occidentalis) or the Kingdom of the West Franks (Latin: regnum Francorum occidentalium) refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by "Carl the Great" or Charlemagne. Francia was the forerunner of the future Kingdom of Franceand existed from 843 to 987. [1] West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious. West Francia was the successor of the Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Anglo-Germanic Frankish -dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages . It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty , which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Carl the Great or Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer theRoman Empire from the Byzantine Empire to Western Europe. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire . where Normandy and the Channel Islands rose in power as a key part of the Holy Roman Empire [3]
Prior to Carl the Great, The Merovingian dynasty ([COMMENTedText now]mɛrəˈvɪndʒiən/ ) was
the ruling family of theFranks from around the middle of the
5th The first well-known Merovingian king was Childeric I (died 481). His son Clovis I (died 511) converted to Nicene Christianity , united the Franks and conquered most of Gaul. The Merovingians treated their kingdom as single yet divisible. Clovis's four sons divided the kingdom among themselves, and it remained divided — with the exception of four short periods (558–561, 613–623, 629–634, 673–675) — down to 679. After that it was divided again only once (717–718). The main divisions of the kingdom were Austrasia , Neustria , Burgundy and Aquitaine .
The name Neustria is mostly explained as "new western land", [2] although Taylor (1848) suggested the interpretation of "northeastern land". [3] Nordisk familjebok (1913) even suggested "not the eastern land" ( icke östland ). [4] Augustin Thierry (1825) assumed Neustria is simply a corruption of Westria , from West-rike "western realm". [5] In any case, Neustria contrasts with the name Austrasia "eastern realm". The analogy to Austrasia is even more explicit in the variant Neustrasia . [6] The Kingdom or Domain of Soissons [2] is the historiographical name [3] for the ethnically Roman ,[2]de facto independent remnant of the Western Roman Empire's Diocese of Gaul , which existed during Late Antiquity as an initially nominalenclave and later rump state of the Empire until its conquest by theFranks in AD 486. Its capital was at Noviodunum , today the town of Soissons in France. The rulers of the rump state, notably its final ruler Syagrius , were referred to as "kings of the Romans" (Latin : rex Romanorum ) by the Germanic peoples surrounding Soissons, with the polity itself being identified as the Regnum Romanorum , " Kingdom of the Romans ", by the Gallo-Roman historianGregory of Tours . Whether the title of king was used by Syagrius himself or was applied to him by the barbarians surrounding his realm (in a similar way to how they referred to their own leaders as kings) is unknown. [4]
As for West
Francia, it extended further north and south than modern metropolitan France, but it did not extend as far east but included
Normandy, the Manche and the Channel Islands. It did not include such future French holdings as Lorraine, the County and Kingdom of
Burgundy(the duchy was already a part of West Francia), Alsace and Provence in the east and southeast for example. It also did
not include the Brittany peninsula in the west. In addition, by the 10th
century the authority of the West Frankish monarchs was greatly reduced. This was contrasted by the evergrowing
power of their vassals over their large and usually territorially contiguous fiefs The last Carolingians: Lothair and Louis V The 13-year old Lothair of France inherited all the lands of his father in 954. By this time they were so small that the Carolingian practice of dividing lands among the sons was not followed and his brother Charles received nothing. In 966 Lothair married Emma, stepdaughter of his maternal uncle Otto I. Despite this, in August 978 Lothair attacked the old imperial capital Aachen. Otto II retaliated by attacking Paris, but was defeated by the combined forces of king Lothar and nobles and peace was signed in 980, ending the brief Franco-German war. Lothar managed to increase his power, but this was reversed with the coming of age of Hugh Capet, who began forming new alliances of nobles and eventually was elected as king in 987 after Lothair and his son and successor Louis V of France had both died prematurely, traditionally marking the end of the French branch of Carolingian dynasty as well as the end of West Francia as a kingdom in the hands of Carolingians. Hugh Capet would be the first ruler of a new royal house, the House of Capet, who would rule France through the High Middle Ages.
Description of the Lords of The European Fief of Blondel and Eperons - Est. 1179 Commissioner George Mentz is the Seigneur of the Fief Blondel & Eperons of Normandy which is an 800 year old territory on the Norman Islands. From the great Viking Rollo to the present day of the rule of King Charles, these islands have allowed feudal law and courts on the fiefs and island shores. The Fief Blondel and Eperons and its Seigneur are registered directly with the Royal Courts of the Crown and The Duke of Normandy and King Charles. Much like the Seigneurs of Monaco, the lords of French Andorra, Sovereign Gozo of Malta, the Sovereign Military Order of Malta (SMOM), The Papal Monarch of the Vatican City, and The Lord of Sark, The ancient Fiefs in the Channel islands are recognized by both nobility law and international law. Commissioner Dr. George Mentz was elevated as the 26th Free Lord & Seigneur of Fief of Blondel et L'Epersons) on the island of (Dgèrnésiais - Guernsey French) in Dec. 2017. Mentz also registered the fief direct with the courts using the feudal legal system of Conge and Tresieme which is the official way to transfer a fief from one noble leader or peer to another owner. The Fief of Thom. Blondel is One of the Last Great Private Fiefs in Europe to be privately owned where the lord owns the Beaches, Water, Foreshores and Seasteds including international Waters. In other local cultures, the free-lord Seigneur is known as a Frhr. Friherre in Sweden, a Frhr. Vrijheer in Dutch, and a Frhr. Friherre in Denmark. The Lords of Fief Blondel et Eperons appear to be older than the Seigneurs of Monaco as the Grimaldi family settled in Monaco in 1297 and Fief Blondel is also older than ancient Sheikhdom of Kuwait, Kingdom of Moscovy Russia 1362, Kingdom of Spain 1479, Kingdom of Bohemia, Kingdom of Belgium. Fief Blondel may also be older than the Ottoman Empire, Habsburg Empire, and the Kingdom of Lithuania. French: Le commissaire George Mentz est le seigneur du fief Blondel & Eperons de Normandie, un territoire vieux de 800 ans situé sur les îles normandes. Du grand Viking Rollo jusqu'à l'époque actuelle du règne du roi Charles, ces îles ont permis l'application du droit féodal et des tribunaux sur les fiefs et les côtes des îles. Le fief Blondel et Eperons ainsi que son seigneur sont enregistrés directement auprès des Cours Royales de la Couronne, du Duc de Normandie et du Roi Charles. Tout comme les seigneurs de Monaco, les seigneurs de la France, Andorre, le Souverain Gozo de Malte, l'Ordre Souverain Militaire de Malte (SMOM), le Monarque Papal de la Cité du Vatican et le Seigneur de Sark, les anciens fiefs des îles de la Manche sont reconnus à la fois par le droit de la noblesse et par le droit international. Le commissaire George Mentz a été élevé au rang de 26ème Seigneur Libre et Seigneur du fief de Blondel et L'Epersons) sur l'île de (Dgèrnésiais - français de Guernesey) en décembre 2017. Mentz a également enregistré le fief directement auprès des tribunaux en utilisant le système juridique féodal de Conge et Tresieme, qui est la manière officielle de transférer un fief d'un noble leader ou pair à un autre propriétaire. Le fief de Thom. Blondel est l'un des derniers grands fiefs privés en Europe à être la propriété privée où le seigneur possède les plages, l'eau, les rivages et les estrades maritimes, y compris les eaux internationales. Dans d'autres cultures locales, le seigneur libre Seigneur est connu sous le nom de Frhr. Friherre en Suède, un Frhr. Vrijheer en néerlandais, et un Frhr. Friherre au Danemark. Les seigneurs du fief Blondel et Eperons semblent être plus anciens que les seigneurs de Monaco car la famille Grimaldi s'est installée à Monaco en 1297 et le fief Blondel est également plus ancien que l'ancien émirat du Koweït, le royaume de Moscovy Russie 1362, le royaume d'Espagne 1479, le royaume de Bohème, le royaume de Belgique. Le fief Blondel pourrait également être plus ancien que l'Empire ottoman, l'Empire des Habsbourg et le royaume de Lituanie. German: Kommissar George Mentz ist der Seigneur des Fiefs Blondel & Eperons der Normandie, das ein 800 Jahre altes Territorium auf den Normanneninseln ist. Von dem großen Wikinger Rollo bis zur heutigen Zeit unter der Herrschaft von König Charles haben diese Inseln feudales Recht und Gerichte auf den Lehen und Inselküsten ermöglicht. Das Fief Blondel und Eperons sowie sein Seigneur sind direkt bei den Königlichen Gerichten der Krone, dem Herzog der Normandie und König Charles registriert. Ganz ähnlich wie die Seigneurs von Monaco, die Herren von Frankreich, Andorra, dem Souveränen Gozo von Malta, dem Souveränen Militärorden von Malta (SMOM), dem päpstlichen Monarchen des Vatikanstaats und dem Herrn von Sark werden die alten Lehen auf den Kanalinseln sowohl vom Adelsrecht als auch vom Völkerrecht anerkannt. Kommissar Dr. George Mentz wurde im Dezember 2017 zum 26. Freien Herrn & Seigneur des Fiefs von Blondel et L'Epersons) auf der Insel (Dgèrnésiais - Guernsey French) erhoben. Mentz registrierte das Lehen auch direkt bei den Gerichten unter Verwendung des feudalen Rechtssystems von Conge und Tresieme, das die offizielle Art und Weise ist, ein Lehen von einem adligen Führer oder Peer auf einen anderen Eigentümer zu übertragen. Das Fief von Thom. Blondel ist eines der letzten großen privaten Lehens in Europa, das privat besessen ist, wo der Herr die Strände, das Wasser, die Küsten und die Meeresstädte einschließlich der internationalen Gewässer besitzt. In anderen lokalen Kulturen ist der freie Herr Seigneur als Frhr. Friherre in Schweden, ein Frhr. Vrijheer im Niederländischen und ein Frhr. Friherre in Dänemark bekannt. Die Herren des Fiefs Blondel et Eperons scheinen älter zu sein als die Seigneurs von Monaco, da sich die Familie Grimaldi 1297 in Monaco niederließ und das Fief Blondel auch älter ist als das alte Scheichtum Kuwait, das Königreich Moscovy Russland 1362, das Königreich Spanien 1479, das Königreich Böhmen, das Königreich Belgien. Das Fief Blondel könnte auch älter sein als das Osmanische Reich, das Habsburgerreich und das Königreich Litauen. Italian: Il commissario George Mentz è il signore del Feudo Blondel & Eperons della Normandia, un territorio di 800 anni situato nelle isole normanne. Dal grande vichingo Rollo ai giorni nostri sotto il regno di Re Carlo, queste isole hanno permesso l'applicazione della legge feudale e dei tribunali sui feudi e sulle coste delle isole. Il Feudo Blondel ed Eperons e il suo signore sono registrati direttamente presso i Tribunali Reali della Corona, il Duca di Normandia e Re Carlo. Molto simili ai signori di Monaco, i signori della Francia, Andorra, il Sovrano Gozo di Malta, il Sovrano Militare Ordine di Malta (SMOM), il Monarca Papale della Città del Vaticano e il Signore di Sark, gli antichi Feudi delle isole del Canale sono riconosciuti sia dalla legge nobiliare che dal diritto internazionale. Il commissario Dr. George Mentz è stato elevato al rango di 26° Signore Libero & Signore del Feudo di Blondel et L'Epersons) nell'isola di (Dgèrnésiais - Guernsey French) nel dicembre 2017. Mentz ha anche registrato il feudo direttamente presso i tribunali utilizzando il sistema giuridico feudale di Conge e Tresieme, che è il modo ufficiale per trasferire un feudo da un nobile leader o pari a un altro proprietario. Il Feudo di Thom. Blondel è uno degli ultimi grandi feudi privati in Europa a essere di proprietà privata, dove il signore possiede le spiagge, l'acqua, le rive e le città marittime, comprese le acque internazionali. In altre culture locali, il Signore libero Seigneur è conosciuto come Frhr. Friherre in Svezia, un Frhr. Vrijheer in olandese e un Frhr. Friherre in Danimarca. I Signori del Feudo Blondel et Eperons sembrano essere più antichi dei Signori di Monaco, poiché la famiglia Grimaldi si stabilì a Monaco nel 1297 e il Feudo Blondel è anche più antico dell'antico sceicco del Kuwait, del Regno di Moscovia Russia 1362, del Regno di Spagna 1479, del Regno di Boemia, del Regno del Belgio. Il Feudo Blondel potrebbe anche essere più antico dell'Impero Ottomano, dell'Impero degli Asburgo e del Regno di Lituania. Spanish: El comisionado George Mentz es el Señor del Feudo Blondel & Eperons de Normandía, un territorio de 800 años en las Islas Normandas. Desde el gran vikingo Rollo hasta la actualidad bajo el reinado del Rey Carlos, estas islas han permitido la aplicación de la ley feudal y los tribunales en los feudos y las costas de las islas. El Feudo Blondel y Eperons y su Señor están registrados directamente en los Tribunales Reales de la Corona, el Duque de Normandía y el Rey Carlos. Al igual que los Señores de Mónaco, los señores de Francia, Andorra, el Soberano Gozo de Malta, la Orden Militar Soberana de Malta (SMOM), el Monarca Papal de la Ciudad del Vaticano y el Señor de Sark, los antiguos Feudos de las Islas del Canal son reconocidos tanto por la ley nobiliaria como por el derecho internacional. El comisionado Dr. George Mentz fue elevado al rango de 26º Señor Libre y Señor del Feudo de Blondel et L'Epersons) en la isla de (Dgèrnésiais - Guernsey French) en diciembre de 2017. Mentz también registró el feudo directamente en los tribunales utilizando el sistema legal feudal de Conge y Tresieme, que es la forma oficial de transferir un feudo de un líder noble o par a otro propietario. El Feudo de Thom. Blondel es uno de los últimos grandes feudos privados en Europa en ser de propiedad privada, donde el señor posee las playas, el agua, las costas y las ciudades marítimas, incluidas las aguas internacionales. En otras culturas locales, el Señor libre Señor se conoce como Frhr. Friherre en Suecia, un Frhr. Vrijheer en holandés y un Frhr. Friherre en Dinamarca. Los Señores del Feudo Blondel et Eperons parecen ser más antiguos que los Señores de Mónaco, ya que la familia Grimaldi se estableció en Mónaco en 1297 y el Feudo Blondel también es más antiguo que el antiguo jeque del Kuwait, el Reino de Moscovia Rusia 1362, el Reino de España 1479, el Reino de Bohemia, el Reino de Bélgica. El Feudo Blondel también podría ser más antiguo que el Imperio Otomano, el Imperio de los Habsburgo y el Reino de Lituania.
|
FiefSeigneur de la Fief of Blondel Fief Blondel L'Eperons Lord Baron Mentz of Fief Blondel Geurnsey Crown Dependency > Kingdom of West Francia Fief Seigneur Seigneurs and Dames Travel Research Lord Paramount Feudal Barons The Seigneur Order Patron George Mentz Charter of Liberties Deed & Title Fief Blondel Islands Viking Kingdom Fief Worship Fiefs of the Islands ECS Extended Continental Shelf Styles and Dignities Territorial Waters Blondel Privy Seal Fief Bouvees of Fief Thomas Blondel Guernsey Court of Chief Pleas Fief Court Arms Motto Flower Fief de l'Eperon La Genouinne Kingdom of West Francia Fief DuQuemin Bouvée Phlipot Pain Bouvée Torquetil Bouvée Bourgeon Bailiwick of Ennerdale Channel Island History Fief Direct from the Crown A Funny Think Happened On the Way to the Fief Guernsey Bailiwick of Guernsey - Crown Dependency Confederation des Iles Anglo-Normandes Sovereignty Papal Bull Research Links Norse Normandy Order of the Genet Order of the Genet Order of the Star Est. 1022 Knights of theThistle of Bourbon Count of Anjou Fief Rights Blondel and King Richard Press Carnival Manorial Incidents Appointments of Seigneurs Store Portelet Beach Roquaine Bay Neustrasia Columbier Dovecote Fief Blondel Merchandise Fief Blondel Beaches Islands Foreshore Events Fiefs For Sale Sold Lords of Normandy Fief Coin Viscounts de Contentin Fief Blondel Map Feudal Guernsey Titles Board of Trustees The Feudal System Hereditaments Chancellor Flag & Arms Fief Videos Guernsey Castle Sark Contact Advowson Site Map Disclaimer Freiherr Livres de perchage Lord Baron Longford Income Tax Guernsey Valliscaulian Order Saint Benedict of the Celestines Society of Divine Compassion Dictionary Count of Mortain Seigneur de Saint-Sauveur Seigneur of Fief Ansquetil Top Success Books Datuk Seri George Mentz Order St. Benedict OSB Celestines Order of the Iron Crown Order of the White Falcon Colonel Mentz Order Red Eagle Order St. Louis Order Holy Ghost Order of Saint Anthony Order of the Black Swan Order of St Columban Order of the Iron Helmet Livonian Brothers of the Sword Fief treizième and Direct from Crown Scotish Barony Info Prince of Annaly Teffia Ireland Valuation
Feudal Lord of the Fief Blondel of the Nordic Channel Islands Guernsey Est.
1179
Feudalherr - Fief Blondel von der Nordischen Insel Guernsey Est. 1179
New York Gazette - Magazine of Wall Street -
George Mentz -
George Mentz - Aspen Commission - Mentz Arms
Counselor George Mentz Esq. - Seigneur Feif BlondelBaron Annaly Baron Moyashel Grants to Delvin About Longford Styles and Dignities The Seigneur Court Barons Fiefs of the Islands Longford Map The Island Lords Market & Fair Fief Worship Channel Island History Fief Blondel Lord Baron Longford Fief Rights Fief Blondel Merchandise Events Blondel and King Richard Fief Coin Feudal Guernsey Titles The Feudal System Flag & Arms Castle Site Map Disclaimer Blondel Myth DictionaryMentz Scholarship Program 101 Million Donation - Order of the Genet Knighthood |





George Mentz Education -
Commissioner George Mentz
-
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/commissioner-george-mentz-clinches-influencer-180000705.html
-
George Mentz News -
George Mentz Net Worth - George Mentz Noble Tilte -
George Mentz -
George Mentz Trump Commissioner -
George Mentz Freiherren Count Baron -
George Mentz Global Economic Forum -
George Mentz Donates Millions

 century until 751.
century until 751.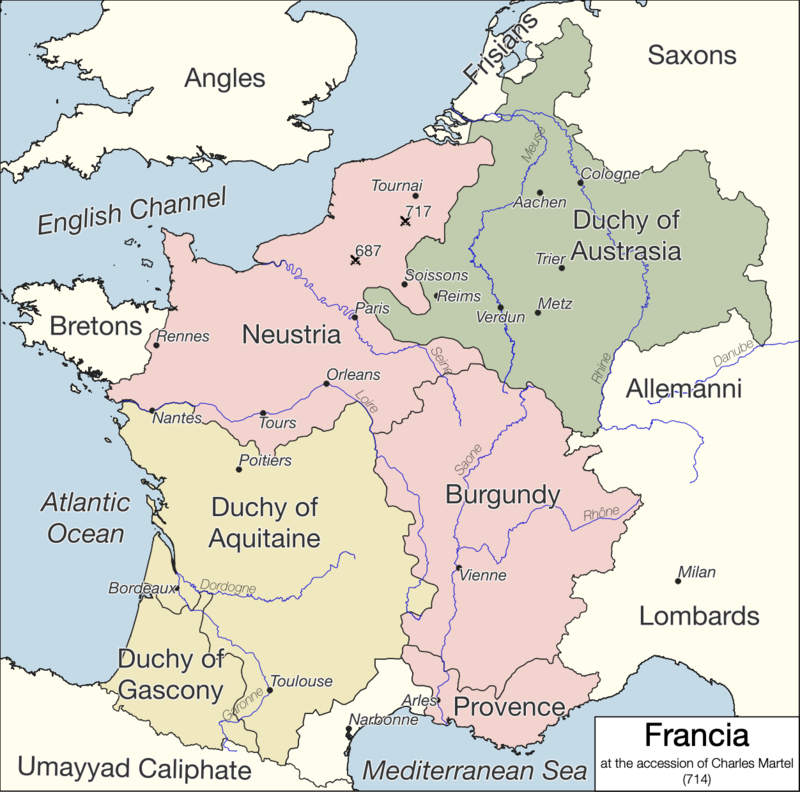
![The Kingdom of Soissons in 476[1] The Kingdom of Soissons in 476[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/5f/Map_of_Gaul%2C_476_AD.png)